Abstract
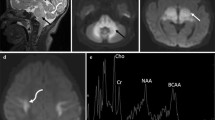
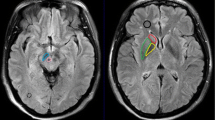
Although conventional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings of glutaric aciduria type 1 (GA-1) have been well established, diffusion weighted MR imaging (DWI) and proton MR spectroscopy (MRS) findings are limited. We report widespread restricted diffusion in the white matter and increased diffusion in bilateral putamen in a case of GA-1. The MRS showed decreased N-acetyl-aspartate (NAA)/creatine (Cr) ratio compared with a sex and age-matched control with no significant change in choline (Cho)/Cr ratio. The presence of the lactate peak reflecting disturbed mitochondrial functions in this disease has never been reported.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goodman SI, Kohlhoff JG (1975) Glutaric aciduria: inherited deficiency of glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase activity. Biochem Med 13:138–140
Haworth JC, Booth FA, Chudley AE et al (1991) Phenotypic variation in glutaric aciduria type 1: report of fourteen cases in five Canadian Indian kindreds. J Pediatr 118:52–58
Kyllerman M, Sten G (1980) Glutaric aciduria: a ‘common’ metabolic disorder? Arch Fr Pediatr 37:279
Monavari AA, Naughten ER (2000) Prevention of cerebral palsy in glutaric aciduria type 1 by dietary management. Arch Dis Child 82:67–70
Bergman I, Finegold D, Gartner JC et al. (1989) Acute profound dystonia in infants with glutaric acidemia. Pediatrics 83:228–234
Forstner R, Hoffman GF, Gassner I et al. (1999) Glutaric aciduria type 1: ultrasonographic demonstration of early signs. Pediatr Radiol 29:138–143
Brismar J, Ozand PT (1995) CT and MR of the brain in glutaric acidemia type 1: a review of 59 published cases and report of 5 new patients. Am J Neuroradiol 16:675–683
Desai NK, Runge VM, Crisp DE, Crisp MB, Naul LG (2003) Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain in glutaric acidemia type 1. A review of the literature and report of four cases with attention to the basal ganglia and imaging technique. Invest Radiol 38:489–496
Twomey EL, Naughten ER, Donoghue VB, Ryan S (2003) Neoroimaging findings in glutaric aciduria type 1. Pediatr Radiol 33:823–830
Brismar J, Ozand PT (1994) CT and MR of the brain in the diagnosis of organic acidemias: experience from 107 patients. Brain Dev 16 (Suppl):104–124
Goodman SI, Nırenberg MD, Shikes RH et al (1977) Glutaric aciduria: biochemical and morphological considerations. J Pediatr 90:746–750
Goodman SI, Markey SP, Moe PT et al (1975) Glutaric aciduria: a new disorder of amino acid metabolism.12:12–21
Lipkin PH, Roe C, Goodman SI, Bathshaw ML (1988) A case of glutaric acidemia type 1: effect of riboflavine and carnithine. J Pediatr 112:62–65
Whetsell WO (1984) The use of organotypic tissue culture for study of amino acid neurotoxicity and antagonism in mammalian. CNS 7:248–250
Mc Donald JW, Johnston MW (1990) Physiological and pathophysiological roles of excitatory amino acids during central nervous system development. Brain Res Rev 15:41–70
Heyes MP (1989) Hypothesis : a role for quinolinic acid in the neuropathy of glutaric aciduria type 1. Am J Neurol 8:441–443
Moller HE, Koch HG, Weglage J, Freudenberg F, Ullrich K (2003) Investigation of the cerebral energy status in patients with glutaric aciduria type 1 by 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Neuropediatr 34:57–60
Bahr O, Mader I, Zschocke J, Dichgans J, Schulz JB (2002) Adult onset glutaric aciduria type 1 presenting with leucoencephalopathy. Neurology 59:1802–1804
Elster AW (2004) Glutaric aciduria type 1. Value of diffusion weighted magnetic resonance ımaging for diagnosing acute striatal necrosis. J Comput Assist Tomogr 28:98–100
Sander JA (1995) Magnetic resonance spectroscopy. In: Orrison WW, Lewine JD, Sanders JA, Harthshorne MF (eds) Functional brain imaging. Mosby, St Louis, pp 419–467
Miller BL (1991) A review of chemical issues in 1H NMR spectroscopy: N-acetyl-L-aspatate, creatine, and choline.NMR Biomed 4:47–52
Sener RN (2003) Canavan disease. Diffusion MR ımaging findings. J Comput Assist Tomogr 27:30–33
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oguz, K.K., Ozturk, A. & Cila, A. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging and MR spectroscopy in glutaric aciduria type 1. Neuroradiology 47, 229–234 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-005-1350-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-005-1350-3